9.9 KiB
Hot Reloading ("Live" Development)
Summary
When developing in debug-builds with the nightly toolchain, conduwuit is modular
using dynamic libraries and various parts of the application are hot-reloadable
while the server is running: http api handlers, admin commands, services,
database, etc. These are all split up into individual workspace crates as seen
in the src/ directory. Changes to sourcecode in a crate rebuild that crate and
subsequent crates depending on it. Reloading then occurs for the changed crates.
Release builds still produce static binaries which are unaffected. Rust's soundness guarantees are in full force. Thus you cannot hot-reload release binaries.
Requirements
Currently, this development setup only works on x86_64 and aarch64 Linux glibc.
musl explicitly does not support hot reloadable libraries, and does not
implement dlclose. macOS does not fully support our usage of RTLD_GLOBAL
possibly due to some thread-local issues. This Rust issue may be of
relevance, specifically this comment. It may be possible to get it working
on only very modern macOS versions such as at least Sonoma, as currently loading
dylibs is supported, but not unloading them in our setup, and the cited comment
mentions an Apple WWDC confirming there have been TLS changes to somewhat make
this possible.
As mentioned above this requires the nightly toolchain. This is due to reliance
on various Cargo.toml features that are only available on nightly, most
specifically RUSTFLAGS in Cargo.toml. Some of the implementation could also be
simpler based on other various nightly features. We hope lots of nightly
features start making it out of nightly sooner as there have been dozens of very
helpful features that have been stuck in nightly ("unstable") for at least 5+
years that would make this simpler. We encourage greater community consensus to
move these features into stability.
This currently only works on x86_64/aarch64 Linux with a glibc C library. musl C
library, macOS, and likely other host architectures are not supported (if other
architectures work, feel free to let us know and/or make a PR updating this).
This should work on GNU ld and lld (rust-lld) and gcc/clang, however if you
happen to have linker issues it's recommended to try using mold or gold
linkers, and please let us know in the conduwuit Matrix room the linker
error and what linker solved this issue so we can figure out a solution. Ideally
there should be minimal friction to using this, and in the future a build script
(build.rs) may be suitable to making this easier to use if the capabilities
allow us.
Usage
As of 19 May 2024, the instructions for using this are:
-
Have patience. Don't hesitate to join the conduwuit Matrix room to receive help using this. As indicated by the various rustflags used and some of the interesting issues linked at the bottom, this is definitely not something the Rust ecosystem or toolchain is used to doing.
-
Install the nightly toolchain using rustup. You may need to use
rustup override set nightlyin your local conduwuit directory, or usecargo +nightlyfor all actions. -
Uncomment
cargo-featuresat the top level / root Cargo.toml -
Scroll down to the
# Developer profilesection and uncomment ALL the rustflags for each dev profile and their respective packages. -
In each workspace crate's Cargo.toml (everything under
src/*ANDdeps/rust-rocksdb/Cargo.toml), uncomment thedylibcrate type under[lib]. -
Due to this rpath issue, you must export the
LD_LIBRARY_PATHenvironment variable to your nightly Rust toolchain library directory. If using rustup (hopefully), use this:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$HOME/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/lib/ -
Start the server. You can use
cargo +nightly runfor this along with the standard. -
Make some changes where you need to.
-
In a separate terminal window in the same directory (or using a terminal multiplexer like tmux), run the build Cargo command
cargo +nightly build. Cargo should only rebuild what was changed / what's necessary, so it should not be rebuilding all the crates. -
In your conduwuit server terminal, hit/send
CTRL+Csignal. This will tell conduwuit to find which libraries need to be reloaded, and reloads them as necessary. -
If there were no errors, it will tell you it successfully reloaded
#modules, and your changes should now be visible. Repeat 7 - 9 as needed.
To shutdown conduwuit in this setup, hit/send CTRL+\. Normal builds still
shutdown with CTRL+C as usual.
Steps 1 - 5 are the initial first-time steps for using this. To remove the hot reload setup, revert/comment all the Cargo.toml changes.
As mentioned in the requirements section, if you happen to have some linker
issues, try using the -fuse-ld= rustflag and specify mold or gold in all the
rustflags definitions in the top level Cargo.toml, and please let us know in
the conduwuit Matrix room the problem. mold can be installed typically
through your distro, and gold is provided by the binutils package.
It's possible a helper script can be made to do all of this, or most preferably
a specially made build script (build.rs). cargo watch support will be
implemented soon which will eliminate the need to manually run cargo build all
together.
Addendum
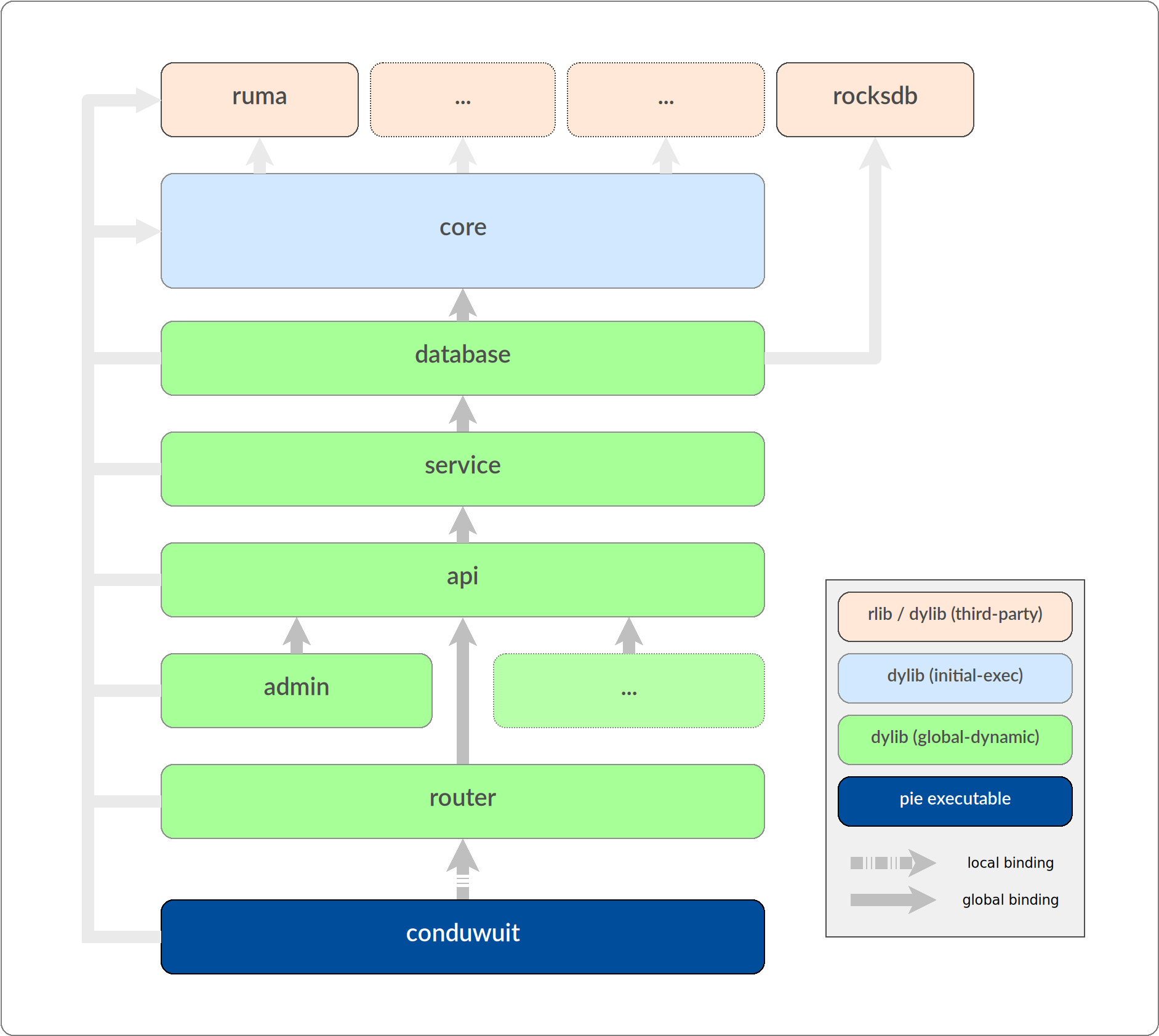
Conduit was inherited as a single crate without modularity or reloading in its design. Reasonable partitioning and abstraction allowed a split into several crates, though many circular dependencies had to be corrected. The resulting crates now form a directed graph as depicted in figures below. The interfacing between these crates is still extremely broad which is not mitigable.
Initially hot_lib_reload was investigated but found appropriate for a
project designed with modularity through limited interfaces, not a large and
complex existing codebase. Instead a bespoke solution built directly on
libloading satisfied our constraints. This required relatively minimal
modifications and zero maintenance burden compared to what would be required
otherwise. The technical difference lies with relocation processing: we leverage
global bindings (RTLD_GLOBAL) in a very intentional way. Most libraries and
off-the-shelf module systems (such as hot_lib_reload) restrict themselves
to local bindings (RTLD_LOCAL). This allows them to release software to
multiple platforms with much greater consistency, but at the cost of burdening
applications to explicitly manage these bindings. In our case with an optional
feature for developers, we shrug any such requirement to enjoy the cost/benefit
on platforms where global relocations are properly cooperative.
To make use of RTLD_GLOBAL the application has to be oriented as a directed
acyclic graph. The primary rule is simple and illustrated in the figure below:
no crate is allowed to call a function or use a variable from a crate below
it.
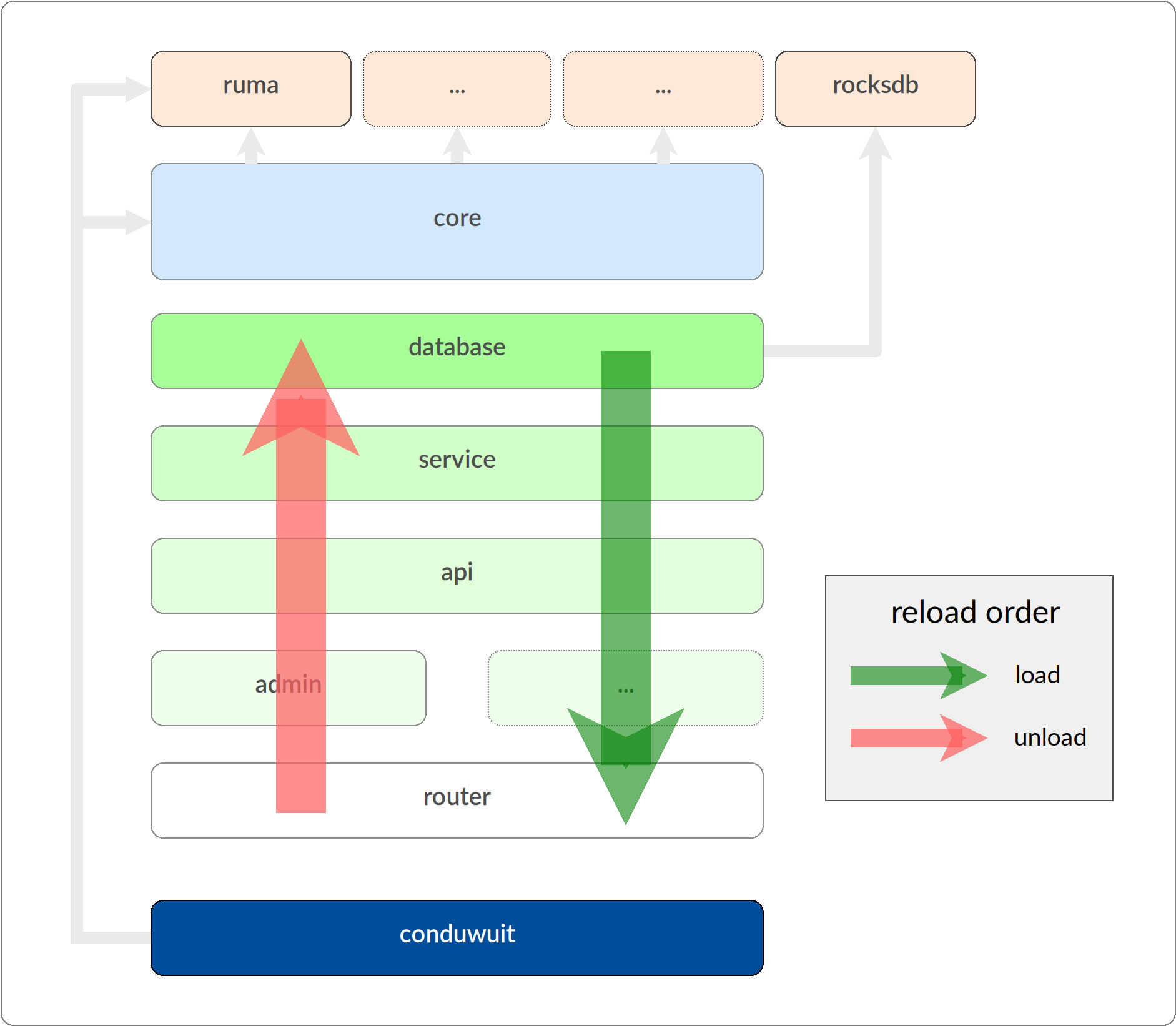
When a symbol is referenced between crates they become bound: crates cannot be
unloaded until their calling crates are first unloaded. Thus we start the
reloading process from the crate which has no callers. There is a small problem
though: the first crate is called by the base executable itself! This is solved
by using an RTLD_LOCAL binding for just one link between the main executable
and the first crate, freeing the executable from all modules as no global
binding ever occurs between them.
Proper resource management is essential for reliable reloading to occur. This is a very basic ask in RAII-idiomatic Rust and the exposure to reloading hazards is remarkably low, generally stemming from poor patterns and practices. Unfortunately static analysis doesn't enforce reload-safety programmatically (though it could one day), for now hazards can be avoided by knowing a few basic do's and dont's:
-
Understand that code is memory. Just like one is forbidden from referencing free'd memory, one must not transfer control to free'd code. Exposure to this is primarily from two things:
- Callbacks, which this project makes very little use of.
- Async tasks, which are addressed below.
-
Tie all resources to a scope or object lifetime with greatest possible symmetry (locality). For our purposes this applies to code resources, which means async blocks and tokio tasks.
- Never spawn a task without receiving and storing its JoinHandle.
- Always wait on join handles before leaving a scope or in another cleanup function called by an owning scope.
-
Know any minor specific quirks documented in code or here:
- Don't use
tokio::spawn, instead use ourHandleincore/server.rs, which is reachable in most of the codebase viaservices()or other state. This is due to some bugs or assumptions made in tokio, as it happens inunsafe {}blocks, which are mitigated by circumventing some thread-local variables. Using runtime handles is good practice in any case.
- Don't use
The initial implementation PR is available here.